Hashing in Blockchain: How Does It Secure the Network?

In a digital trust world, the security of blockchain technology lies within a single, amazing tool: hashing in blockchain. Think of it as a unique digital fingerprint or signature that guarantees every piece of data on the blockchain is unique, authentic, and secure. Without hashing in blockchain, the system would be just a database. But with it, it becomes an invincible chain of truth.
Whether you’re transferring cryptocurrency, verifying a transaction, constructing a smart contract, or performing a variety of other operations, hashing in blockchain operates quietly in the background to maintain the security and authenticity of all those activities. We’ll take a look at what a hash is in blockchain, how hashing in blockchain works, and its important role in launching blockchain to game-changing digital security in this article. Let’s get started!
Hash in Blockchain—What is it?
On the blockchain, hashing in blockchain creates a special type of digital fingerprint called a hash that guarantees the authenticity of data. It’s generated by a process such as SHA-256, a mathematical algorithm that can take any input, such as a text passage, a file, or an image, and turn it into a unique string of characters of a fixed length, called a “hash value”.
This hash is specific to the input, and hashing in blockchain ensures that changing the source data produces a new hash—a property called the “avalanche effect.”One of the most vital properties of hashing is that it’s a one-way function—it’s relatively easy to compute the hash value for a given set of data, but it’s nearly impossible to create a set of data that would have a given hash value. This has the advantage of being very reliable in verifying data without leaking the information itself. In the context of blockchain, hashing is used to link blocks securely so that they cannot be tampered with, and trust can be passed across multiple decentralized networks.
How Does Hashing Work in Blockchain—Explained
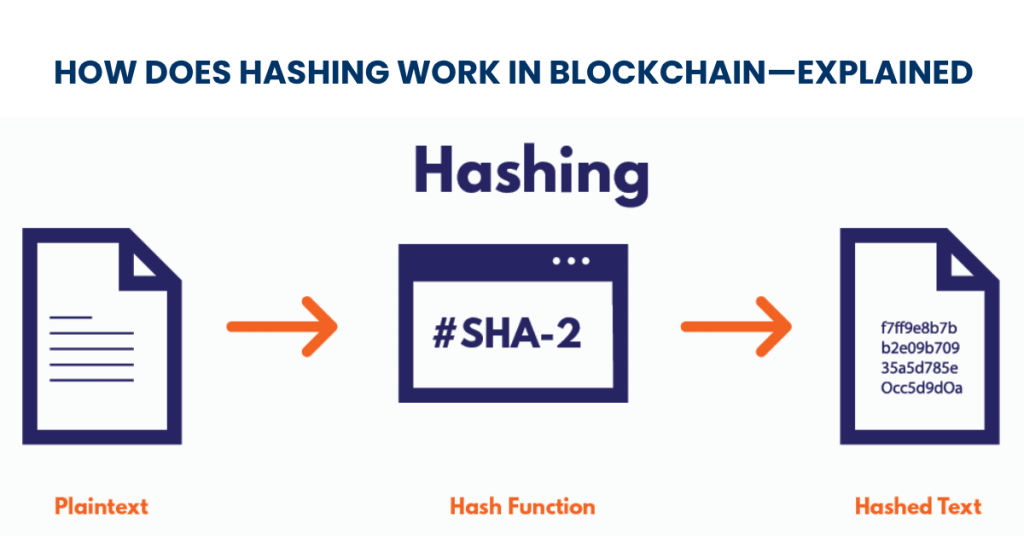
At a basic level, hashing in blockchain represents the process of using a cryptographic algorithm, such as the SHA-256 algorithm, on input data to generate a predetermined-length (and usually unique) string of characters called a hash value. And the process is one-way, which means that once the hash is created, it’s virtually impossible to find out the original input; that’s why it’s perfect for secure data recording.
In a blockchain, each block has several things: transaction data, a timestamp, its hash, and a hash of the previous block. These hashes connect blocks in a secure and time-ordered chain. If any information in a block is changed, the hash of that block changes; however, the hash in the next block does not. It would take an amount of computation to recalculate the hashes of all following blocks, rendering tampering all but impossible.
Hashing in blockchain is also one component of consensus protocols such as Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). In PoW miners hash block data with various random data over and over until they reach a hash result (meeting the targeted criteria)—a process that secures the network and checks transactions. In PoS, validators rely on hashing to validate the authenticity of data and to arrive at consensus throughout the entire network.
Put simply, hashing in blockchain is the reason blockchain networks are considered secure, transparent, and trustworthy. It serves multiple purposes, including the preservation of the block structure, the authentication of transactions, the prevention of fraudulent behaviours, and the maintenance of decentralization properties among involved participants.
What Are the Uses of Hashing in Blockchain?

Hashing changes data to a special hash, where too many characters are used without the same for the data, which allows for the decentralization, integrity of data and transactions, and other key aspects of blockchain. In this part, we will take a look at the most common uses of hashing in blockchain:
1. Immutability: One of the most important capabilities of hashing in blockchain is its immutability. A hash is a “one-way function” that, if data is written, can’t be reversed or modified. In public blockchains such as Bitcoin, each transaction is connected to a unique hash. If you attempt to change any piece of data in that block, even so much as a semicolon, you’d have to recalculate the ‘hash’ of that block and all subsequent blocks, which simply is not feasible in terms of modern computation.
2. Fast & Secure Transaction Verification: Hashing in blockchain allows for fast transaction verification. Every transaction is assigned a unique hash by functions such as SHA-256. Upon transaction receipt, the involved parties compare the new hash to the previous one on the blockchain. A valid transaction is one where both of them match. This way, the network is kept on consensus, and only real, unaltered transactions are added to the blockchain.
3. Data Fingerprinting: Hashing in blockchain serves as a digital imprint for each piece of data appearing in the blockchain. It turns data, such as messages, transactions, or entire blocks, into a unique hash value that provides a checksum. The smallest alteration to data results in a completely different hash. This makes it simple for users, miners, or validators to ascertain that the data has not been tampered with, effectively proving the authenticity and trustworthiness across the network.

4. Decentralization: Hashing in blockchain is essential for the decentralized consensus mechanisms of the blockchain, in particular models such as the Proof of Work (PoW). Miners compete to solve the problems, finding a type of hash that meets a central authority’s criteria, which permits them to add new blocks to the chain. This is what guarantees that transaction validation is conducted by several separate participants, which means that no one entity can dominate the network.
5. Smart Contracts Security: Hashing in blockchain plays an integral role in securing smart contracts, which are self-operating contracts with a specific set of rules. A smart contract has a unique hash to prove it hasn’t been tampered with. If anything is changed in that contract code, the hash will also change, informing users of attempted modifications immediately. This secures programmable contracts and ensures that they work just as they are programmed.
6. Digital Signatures: Hashing in blockchain is fundamental to digital signatures, which are essential for identity provision on the blockchain. When the user signs the transaction with his or her private key, a hash of the data is generated and sent with the transaction. Allowing them to be confident that only the actual owner ever authorised the transaction.
7. On-Chain Data Verification: People often use a blockchain to verify some external or off-chain data without needing to store the full dataset on-chain. This can be achieved through data anchoring, which is the practice of hashing in blockchain to secure original data and then storing only the hash on the blockchain. Then, anyone can rehash the original file and compare it to the on-chain hash to verify that the data has not been changed.
Wrapping Up
In the end, hashing is the tool that makes blockchain security, speed, and trust tick. Whether used to protect the integrity of your data or to create records that can be impossible to tamper with, whether for smart contracts or digital signatures, hashing verifies and secures every block and transaction. Being a one-way, fixed-output operation, it is infeasible for the attacker to reverse-engineer or modify the blockchain data. Be it for proving off-chain facts or ensuring decentralized consensus, hashing is at the core of why blockchains are trusted at all. Because blockchain technology is still relatively developing, hashing is becoming increasingly more prominent and essential as time advances.
Read More:
FAQs—How Does a Hash Help Secure Blockchain Technology?
1. What is a block in Blockchain technology?
In blockchain, a hash is a string of characters produced by a cryptographic algorithm to define a dataset. It serves as a digital seal on the data, a guarantee that it has not been altered. It has this amazing property that even the slightest alteration to its original input leads to a totally different hash, making it an excellent way to detect tampering or changes in the context of blockchains.
2. Why is hashing so important for blockchain protection?
Hashing is important because it makes it so that once you put data in a block, you can’t change it, at least without altering all of the blocks that come after it –something that’s computationally impossible. This attribute helps to prove immutability, prevent fraud and build trust from users in that the data on the blockchain is secure and cannot be tampered with.
3. How does a hash help to keep blockchain data secure and immutable?
A block in a blockchain has its own hash and the hash of the block before it. Altering any data inside a block causes the hash of the block to change, thereby breaking its link on the chain.
4. What’s the popular hash function in blockchains?
The hashing algorithm Bitcoin uses is SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256-bit). Security, fast, no collision, and no reverse engineering have made the SHA-256 hash algorithm a broad application for many decentralized networks such as Bitcoin.
5. Can a hash value be decrypted back to the original data?
No, a hash is not reversible. The hash function itself is one-way: that is, it always produces an identical hash output from an input, and there is no way to recover the input data from the hash. This one-directional process is essential for the security of blockchain systems.
6. What is the purpose of hashing in Proof-of-work consensus algorithms?
In Proof of Work (PoW), miners are competing to solve a cryptographic puzzle by finding a hash that satisfies certain conditions. This is called mining and it protects the network and creates new blocks in the chain.










One Comment